
Expiration is primarily a passive process (i.e.Air reaches the respiratory zone of the respiratory tree (site of gas exchange): respiratory bronchioles → alveolar ducts → alveoli.Intrathoracic pressure becomes even more negative to fill the lungs with air.Inspiratory muscles (mainly external intercostal muscles and the diaphragm) elevate the ribs and sternum and increase the intrathoracic volume.Inspiration of air into the conducting zone of the respiratory tree ( anatomic dead space): nose → pharynx → larynx → trachea → bronchi → bronchioles → terminal bronchioles.Definition: movement of air through the respiratory tract into (inspiration) and out of (expiration) the respiratory zone ( lungs) to facilitate gas exchange (O 2 and CO 2).Inspiration is an active process driven by the respiratory musculature while expiration is passive at rest, driven by the elastic properties of lung tissue. Central regulation of respiration is provided by the respiratory center located in the reticular formation of the medulla oblongata and pons. CO 2 diffuses into the alveoli and is exhaled. In the capillaries, oxygen binds to hemoglobin in erythrocytes or dissolves into the plasma (oxygenation). The gases diffuse across the barrier following pressure gradients. Gas exchange occurs via simple diffusion across the blood-air barrier. Diseases that affect the perfusion (e.g., pulmonary embolism) or ventilation (e.g., foreign body aspiration) can cause a V/Q mismatch.
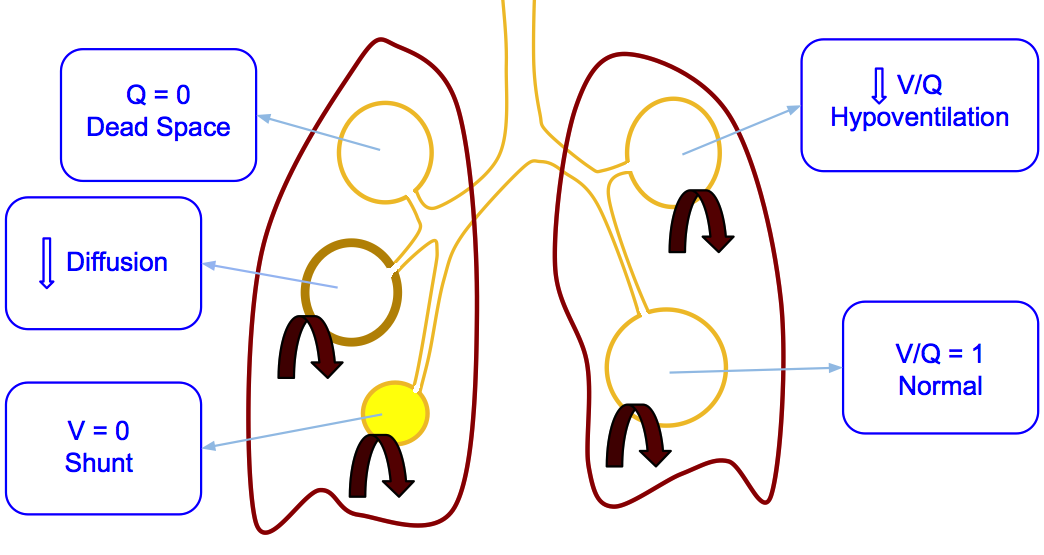
The Euler-Liljestrand mechanism regulates the perfusion of nonventilated alveoli: if a lung section is perfused but not ventilated, there will be a drop in the oxygen concentration in the blood, resulting in hypoxic vasoconstriction. The ventilation-perfusion ratio is higher in the apex of the lung than at its base. Perfusion of the pulmonary capillaries is closely regulated to match ventilation in order to maximize gas exchange. The physiologic dead space is the volume of inspired air that does not participate in gas exchange. Ventilation is the movement of air through the respiratory tract into (inspiration) and out of (expiration) the respiratory zone ( lungs). The main function of the respiratory system is gas exchange (O 2 and CO 2).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
